Visual Learning Appified (VLA) illustrates visual skills required for learning through fun activities. If your child has difficulties with the activities, you can use the App to find your local Paediatric optometrists and contact them to make an appointment.
Paediatric optometrists not only check for good eyesight and eye health but also check for poor visual perception and cognition. These skills are sufficiently associated with reading achievement and ability (1). The three activities in the VLA are Visual Sequential Memory, Visual Memory and Auditory Visual Integration and are modeled on real clinical tests.
Visual Sequential Memory is strongly tried with the use of language to organise, store, rehearse and recall of visual information and has been found to be effective in identifying learning disabled and normal children (2,3,4). The activity is based on the Test of Visual Perceptual Skills and requires the child to memorise a sequence of objects.
Visual memory helps expands a child’s vocabulary of sight words. Difficulty with this results in phonetic spelling i.e. laf for laugh (5). It is also related to visual processing speed, which is worse in dyslexics (6). The activity is based on the Ravens Pattern Matching Test and requires the child to match the missing piece of the puzzle.
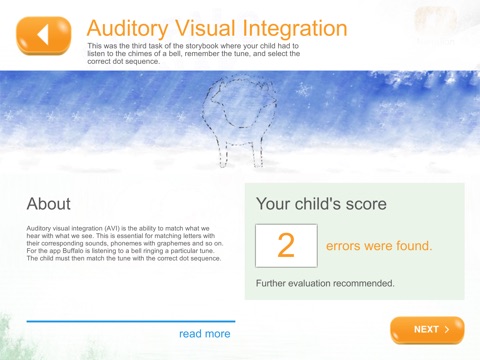
Auditory visual integration is the ability to match auditory stimuli with its visual representation. It correlates very well with reading performance up to the age of eight (7). A child who has difficulty with this activity could have poor attention, memory, decoding, temporal and sequential processing and needs to be assessed. The activity is based on the Birch & Belmont AVIT and requires the child to match the correct dot patterns to the sound pattern.
REFERENCE:
- Watson BU, Goldgar DE. Subtypes of reading disability: A combination of visual motor skill, visual perceptual skills contribute to reading disability. J Clin Neuropscyhol 1983;5: 377-399
- Bryant ND. Characteristics of dyslexia and their remedial implications. Except Child 1964; 31:195-200
- Kass CD. Psycholinguistic disabilities of children with reading problems. Except Child 1966; 32: 533-9
- Amoriell WJ. Reading achievement and the ability to manipulate visual and auditory stimuli. J Learn Disabil 1979; 12: 562-6
- Scheiman MM, Rouse MW. Optometric Management of Learning Related Vision Problems. 2nd Edition. Elsevier 2006
- Orton ST. Specific reading disability – strephosymbodlia. JAMA 1928; 90: 1090-9
- Birch HG, Belmont L. Auditory visual integration, intelligence, and reading ability in school children. Percep Mot Skills 1965;20: 295-3